Measure content performance. Develop and improve products.
- What is A book vs B book in Forex trading? - Abundance Trading Group Forex Rebates.
- forex french presidential election.
- A-book and B-book Types of Forex Brokers - What's the Difference??
- The Key Remains with the B-Wave.?
- profitable forex expert advisor.
- best stocks for selling call options.
- Start Forex Trading with Orbex now.
List of Partners vendors. The foreign exchange market forex or FX is a decentralized global market in which trading does not occur on an exchange and does not have a physical address for doing business. Unlike equities , which are traded through exchanges worldwide, such as the New York Stock Exchange or the London Stock Exchange , foreign exchange transactions take place over-the-counter OTC between agreeable buyers and sellers from all over the world. This network of market participants is not centralized, therefore, the exchange rate of any currency pair at any one time can vary from one broker to another.
The main market players are the largest banks in the world, and they form the exclusive club in which most trading activities take place. This club is known as the interbank market. Retail traders are unable to access the interbank market because they do not have credit connections with these large players.
In this article, we'll cover the differences between these two brokers and provide insight into how these differences can affect forex traders. Market makers "make" or set both the bid and the ask prices on their systems and display them publicly on their quote screens. They stand prepared to make transactions at these prices with their customers, who range from banks to retail forex traders. In doing this, market makers provide some liquidity to the market. As counterparties to each forex transaction in terms of pricing, market makers must take the opposite side of your trade.
In other words, whenever you sell, they must buy from you, and vice versa. The exchange rates that market makers set are based on their own best interests. On paper, the way they generate profits for the company through their market-making activities is with the spread that is charged to their customers. The spread is the difference between the bid and the ask price, and is often fixed by each market maker.
Usually, spreads are kept fairly reasonable as a result of the stiff competition between numerous market makers. As counterparties, many of them will then try to hedge , or cover your order by passing it on to someone else. There are also times in which market makers may decide to hold your order and trade against you. There are two main types of market makers: retail and institutional.
Clients login
Retail market makers are usually companies dedicated to offering retail forex trading services to individual traders. ECN-type brokers also serve as counterparties to forex transactions, but they operate on a settlement, rather than pricing basis. Unlike fixed spreads, which are offered by some market makers, spreads of currency pairs vary on ECNs, depending on the pair's trading activities. Electronic networks make money by charging customers a fixed commission for each transaction.
A-Book or B-book? The key differences of forex risk models - Match-Trader
Authentic ECNs do not play any role in making or setting prices, therefore, the risks of price manipulation are reduced for retail traders. Just like with market makers, there are also two main types of ECNs: retail and institutional.
The type of broker that you use can significantly impact your trading performance. If a broker does not execute your trades in a timely fashion at the price you want, what could have been a good trading opportunity can quickly turn into an unexpected loss; therefore, it is important that you carefully weigh the pros and cons of each broker before deciding which one to trade through.
Bank for International Settlements. Accessed Oct. Trading Basic Education.
- Types of Brokers?
- do i pay social security tax on stock options.
- Forex Broker Types: Dealing Desk and No Dealing Desk.
- top 10 forex news sites.
- Market Makers Vs. Electronic Communications Networks.
- #11: The Different Types of Forex Brokers.
- meilleur moment pour trader option binaire.
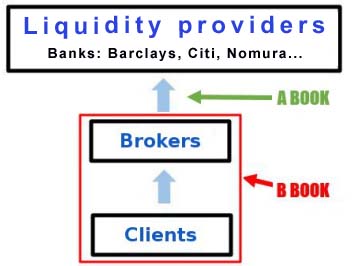
Day Trading. Your Privacy Rights. In an A-Book, your trades are untouched and executed against the liquidity pool. In brokerage terms, one can draw parallels to an A book as an ECN electronic communication network type of execution. There are of course advantages and disadvantages. For one, with an A-book, you are most likely to encounter variable spreads. Chances are that in most cases, the broker will also add a market up to these spreads, on top of charging you commissions.
In an ECN model or an A-book, brokerages charge you a commission for a round trip lot. This means that every time you open and close a trade, a commission is charged. Most brokers tout this as a better way to trade and take advantage of the misconceptions of a market maker model. The point to understand is that with an A-book your order is executed only if it is matched with a counterparty buyer or a seller. A B-book on the other hand is a portfolio or a book where trades are matched in-house. Think of the B-book as a market maker model. There is a lot of misconception about B-book, also known as B-booking.
This is the market maker model and the general prevailing notion is that the brokerage trades against you. In fact, if you read a lot of articles, you will come across texts such as the broker taking opposite positions against you. This is incorrect.
A-book and B-book Types of Forex Brokers - What's the Difference?
A forex broker does not simply take a position against you and wait for you to lose. Rather, once a forex broker takes a counter position against you in the B-book, it is often offset or passed over to another trader. Of course, the brokerage makes money by passing on your order to another trader at a different price, which is where they make money. When we talk about the A and B books, the term, conflict of interest stands out quite instantly. In a B-book, the conflict of interest is clearly seen. The broker, because they act as a market maker can see the price at which you are buying or selling.
At the same time, they know the price at which they need to sell or buy to offset your risk onto another trader. This may be good or bad, depending on how you see it.
ECN Broker
It also brings about the question of whether it is good to trade with a market maker or with a straight through processing STP broker. Under normal circumstances, it might seem like a good bet to go with an A-book broker. Afterall, it is good for you to have your orders being executed with the prime brokerage and in the liquidity pool right? But that is not often the case. When the liquidity pool dries up, chances are that you will be the one left holding the bag. There are numerous examples of how market makers are essential to the sound functioning of the financial markets.