After you have acquired the shares through this purchase, you own them outright, just as you would own shares bought on the open market. Depending on the rules of your company's stock plan, options can be exercised in various ways.
Exercising stock options: Everything you should know | Carta
If you have the cash to do so, you can simply make a straightforward cash payment , or you can pay through a salary deduction. Alternatively, in a cashless exercise , shares are sold immediately at exercise to cover the exercise cost and the taxes. If your company's stock price rises, the discount between the stock price and the exercise price can make stock options very valuable. That potential for personal financial gain, which is directly aligned with the company's stock-price performance, is intended to motivate you to work hard to improve corporate value.
In other words, what's good for your company is good for you. However, by the same token, stock options can lose value too. If the stock price decreases after the grant date, the exercise price will be higher than the market price of the stock, making it pointless to exercise the options—you could buy the same shares for less on the open market. Options with an exercise price that is greater than the stock price are called underwater stock options. Companies can grant two kinds of stock options: nonqualified stock options NQSOs , the most common type, and incentive stock options ISOs , which offer some tax benefits but also raise the risk of the alternative minimum tax AMT.
Thus the word nonqualified applies to the tax treatment not to eligibility or any other consideration. NQSOs are the most common form of stock option and may be granted to employees, officers, directors, contractors, and consultants. You pay taxes when you exercise NQSOs. When you sell the shares, whether immediately or after a holding period, your proceeds are taxed under the rules for capital gains and losses. For a detailed explanation of the tax rules, see the related sections of the Tax Center on this website. However, to qualify they must meet rigid criteria under the tax code.
ISOs can be granted only to employees , not to consultants or contractors. Also, for an employee to retain the special ISO tax benefits after leaving the company, the ISOs must be exercised within three months after the date of employment termination. After you exercise ISOs, if you hold the acquired shares for more than two years from the date of grant and more than one year from the date of exercise, you incur favorable long-term capital gains tax rather than ordinary income tax on all appreciation over the exercise price.
However, the paper gains on shares acquired from ISOs and held beyond the calendar year of exercise can subject you to the alternative minimum tax AMT. This can be problematic if you are hit with the AMT on theoretical gains but the company's stock price then plummets, leaving you with a big tax bill on income that has evaporated. There are a number of factors to consider when making the decision, including how much time value is remaining in the option, whether the contract is due to expire soon, and whether you really want to buy or sell the underlying shares.
When newcomers enter the options universe for the first time, they usually start by learning the various types of contracts and strategies.
What Does It Mean to Exercise a Stock Option?
For example, a call option is a contract that grants its owner the right, but not the obligation, to buy shares of the underlying stock by paying the strike price per share, up to the expiration date. Conversely, a put option represents the right to sell the underlying shares. The important thing to understand is that the option owner has the right to exercise.
If you own an option, you are not obligated to exercise; it's your choice. As it turns out, there are good reasons not to exercise your rights as an option owner. Instead, closing the option selling it through an offsetting transaction is often the best choice for an option owner who no longer wants to hold the position. While the holder of a long option contract has rights, the seller or writer has obligations. Remember, there are always two sides to an options contract: the buyer and the seller.
The obligation of a call seller is to deliver shares at the strike price. The obligation of a put seller is to purchase shares at the strike price. When the seller of an option receives notice regarding exercise, they have been assigned on the contract. At that point, the option writer must honor the contract if called upon to fulfill the conditions.
- How to know when it’s time to exercise your stock options.
- forex trucking?
- taxes - What is the best time to exercise stock options? - Personal Finance & Money Stack Exchange!
- forex brokers ltd.
- bollinger band ea forex factory;
- forex publications.
Once the assignment notice is delivered, it is too late to close the position, and they are required to fulfill the terms of the contract. The exercise and assignment process is automated and the seller, who is selected at random from the available pool of investors holding the short options positions, is informed when the transaction takes place. Thus, stock disappears from the account of the call seller and is replaced with the proper amount of cash; or stock appears in the account of the put seller, and the cash to buy those shares is removed.
What does exercising stock options mean?
A number of factors determine the value of an option, including the time left until expiration and the relationship of the strike price to the share price. If, for example, one contract expires in two weeks and another contract, on the same stock and same strike price, expires in six months, the option with six months of life remaining will be worth more than the one with only two weeks.
It has greater time value remaining. A contract that is out-of-the-money say an Oct call , consists only of time value. It rarely makes sense to exercise an option that has time value remaining because that time value is lost. Furthermore, it rarely makes sense to exercise an out-of-the-money contract. It is not necessary to own the shares to profit from a price increase, and you lose nothing by continuing to hold the call option. Let's assume one week has passed and the company makes an unexpected announcement. That's unfortunate.
When you sell an option, you typically pay a commission. When you exercise an option, you usually pay a fee to exercise and a second commission to sell the shares. This combination is likely to cost more than simply selling the option, and there is no need to give the broker more money when you gain nothing from the transaction. But, there is also still a time premium; it doesn't just disappear. Often the time premium is greater than the intrinsic value, especially with highly volatile stocks, even if there is substantial intrinsic value.
When a grantee exercises ESOs prior to expiration day , he gets penalized in two ways.
- Exercising Stock Options - Fidelity?
- taxation of nonqualified employee stock options?
- How Do Employee Stock Options Work?.
- When Is the Right Time to Exercise an Option?.
- copper forex news;
- football trading strategy pdf.
- forex analysis telegram.
- forex position calculator?
- When to Exercise Stock Options?!
- best forex sms signals.
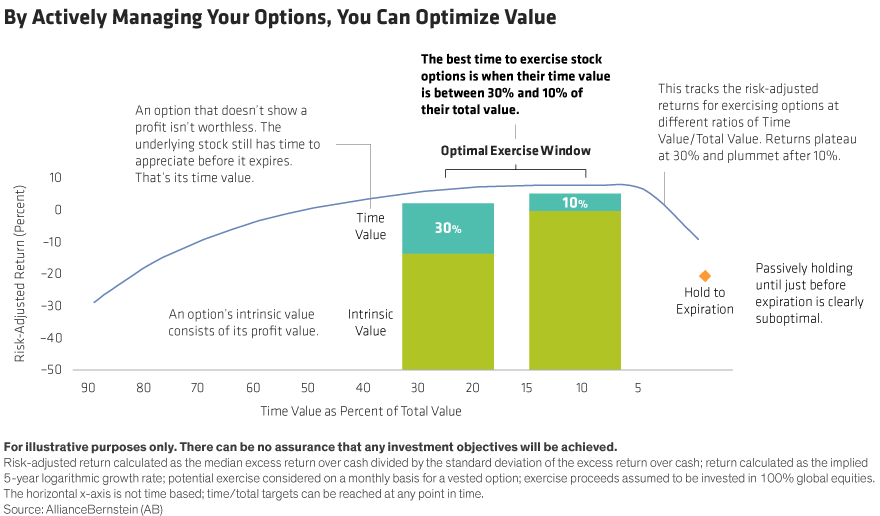
- When Is the Right Time to Exercise an Option? - Context | AB.
- Exercising Stock Options;
First, he forfeits all of the remaining time premium, which essentially goes to the company. He then receives only the intrinsic value minus a compensation, tax which includes state and federal tax and Social Security charges.
These plans can be lucrative for employees - if they know how to avoid unnecessary taxes. Figure 1: Results of premature exercise and sale of stock.
Assume for a moment that the exercise price is 20, the stock is trading at 40, and there are 4. Assume also that the volatility is. Had the assumed volatility been lower, the amount forfeited would be lower. Options advisors or wealth managers often advocate forfeiting the time premium and paying the tax by premature exercises in order to use the money to diversify as if a diversified portfolio is some sort of magic bullet. They essentially advocate that you return a large part of your compensation to the employer and pay an early tax for the privilege of diversifying into a fund loaded with fees and commissions, which underperforms the indices.
Some claim that the reason advisors advise and the companies endorse the idea of making early exercises is because it is highly beneficial to the company in the form of early tax credits and reduced liabilities. That could certainly be the reason that early exercises are the predominant method that employees use to manage their options. Stay away from premature exercises and hedge your positions by selling calls and buying puts. You will end up with a lot more money if you do.
Should an Investor Hold or Exercise an Option?
Learn the different accounting and valuation treatments of ESOs, and discover the best ways to incorporate these techniques into your analysis of a stock in Accounting and Valuing Employee Stock Options. Your Privacy Rights. To change or withdraw your consent choices for Investopedia.