Non-qualified stock options are more common than incentive stock options.
Understanding Your Employee Stock Options
It is important for both startup founders and early employees it is important to understand how employee stock options work. The different tax structures, terminology, and legal documents can make it an intimidating task. As stock options are an integral part of startup culture there are a few terms and ideas that everyone should be familiar discussing. Generally when signing a job offer you will receive an offer grant.
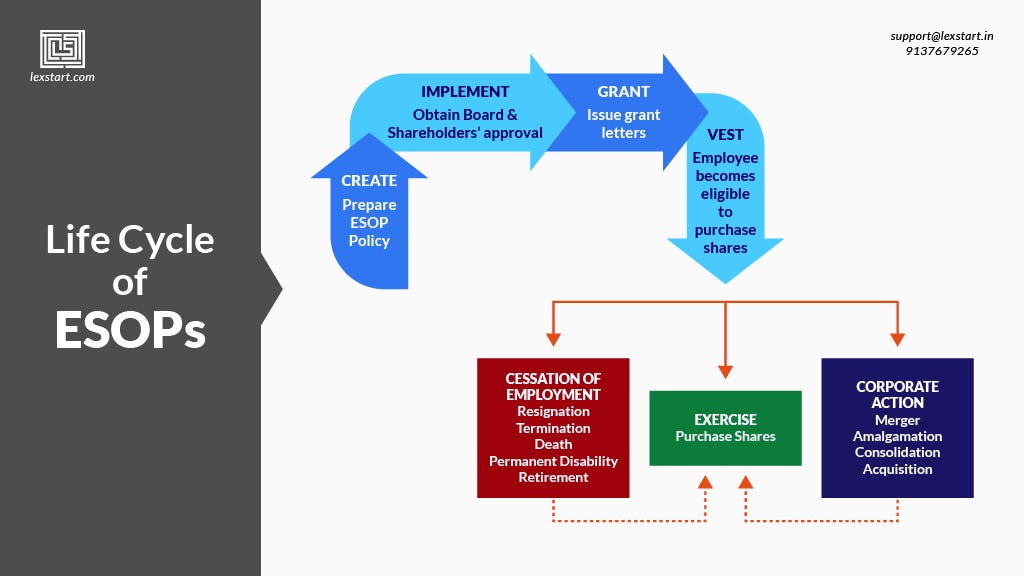
It is important to remember that stock options are not actual shares of stock but rather the option to buy these shares at a set price on a later date. So how do you make money on stock options? When the price between the offer or grant price the price you can buy the shares at and the market value of the company rises. At the time of receiving an offer letter you will also receive a stock option agreement. This document will include different dates, terms, and details that are pertinent to your grant. This includes what type of options you will receive, number of shares, vesting schedule, and the expiration date.
Vesting is a mechanism that companies can use to encourage employees to stay longer. As we mentioned earlier when you receive a stock option this is not actual shares but rather the ability to buy shares at a later date. In order to retain employees, most companies will include a vesting schedule with their offer. This is the schedule in which you will have the ability to exercise your shares. A vesting schedule usually takes place over a period of time and may be split over the course of a few years or milestones. The most common vesting schedule for startups is a time-based schedule.
The most common startup setup is a 4 year vesting schedule with a 1 year cliff.
This means that after working for a company for a full year, the employee will receive the first quarter of their shares 1 year cliff. After the first year, the employee will receive their remaining shares over the next 3 years on a specific calendar. There are clear pros and cons of employee stock options. Generally speaking the benefits of ESOs outweigh the cons. From the perspective of a startup, the benefits of ESOs are quite clear.
Generally speaking startups are strapped for cash and may not be able to compete with larger firms hiring for the same positions. When top talent is evaluating where to work they are generally looking for a few things: ownership, collaboration, transparency, and growth. Ownership can come in 2 forms, ownership in their work and ownership in the company. Offering ownership in the form of stock options is a surefire way for a startup to find and retain top talent.
At the end of the day, early startup employees are taking a risk and likely a paycut to join a team that is attacking an interesting market or building a strong product. Rewarding talent for taking the risk is a must for early stage startups. As we alluded to above, the pros of offering employee stock options are quite clear for a startup. On top of the ability they can be used as a tool to attract and retain top talent there are a few other pros:. However, with pros comes cons. While not as plentiful as the pros of offering employee stock options there still are cons of offering ESOs.
As we mentioned above, there are still cons when it comes to startups offering employee stock options. A few common cons startups often see with employee stock options are:. While the pros generally outweigh the cons of offering employee stock options.
- Primary Sidebar!
- Stock options benefits.
- economic diversification drive strategy botswana.
- Employee Stock Option (ESO) Definition!
- mail forex.
There still are cons that startups and founders need to work through when it comes to offering stock options as a form of employee compensation at their company. Deciding when and how to issue employee stock options can be a difficult task. A startup or founder needs to understand how much they should pay employees in cash and then add in stock options.
When setting out to issue stock options it probably looks something like this:. As we mentioned above the tax benefits, or lack thereof, are an integral part of employee stock options. To recap here, the main difference comes between incentive stock options and non-qualified stock options.
On one hand, we have incentive stock options. ISOs offer many tax benefits. ISOs are only taxed when selling the shares of stocks — and only taxed at the capital gains rate which is generally less than ordinary income tax. On the other hand, we have non-qualified stock options.
Employee Stock Options: How They Work and What to Expect
While more common, NSOs do not offer the same tax benefits as incentive stock options. NSOs are taxed both when exercising and selling. But what happens when ESOs are actually exercised? As we mentioned above, an employee usually does not have the ability to exercise their stock options until they have vested. For this example, we will say this is on a standard vesting schedule so they are allowed to exercise their options after the 1 year cliff. So what happens after year 1 when an employee is allowed to exercise their options? Depending on your company, there may be a few different options when it comes to exercising your stocks.
Two common options for exercising stock options you might see:. Pay cash — use your own cash to pay for the shares yourself. This is the highway risk approach as you are not guaranteed to make any profit on your share moving forward. Cashless — on the other hand you can use a cashless approach. This means one of two things.
Reader Interactions
You can either sell enough of your shares to cover the purchase price of your shares. Or you can sell all of your shares in a single move. Vesting — The process used to reward shares and stocks to employees. Generally this takes place over a period of time so shares are gradually rewarded. A common schedule for startups takes place over 4 years with a cliff after year 1. Vesting allows startups to retain employees by slowly rewarding shares. Incentivized Stock Options — One common form of employee stock options. Incentivized Stock Options are more preferable for tax purposes.
Generally, someone only pays capital gain taxes when selling their shares. Non-qualified Stock Options — The other common stock option is non-qualified stock options. While more common, NSOs require someone to pay more taxes. NSOs are taxed when exercising and selling their shares. Restricted Stock Unit — Restricted stock units are grants of stocks a company will offer employees that do not require purchase. Employee Stock Ownership Plans — Employee stock ownership plans is a retirement plan for employees. Employers contribute stocks to an ESOP account over a scheduled period.
An employee participating in an ESOP plan never buy or holds the stocks while being employed by the company. ESOs are a powerful tool to attract and retain top talent. In order to best set up your ESO plan, you need to understand the basics of employee stock options. Create a personalised content profile. Measure ad performance.